Metallfertigteilgebäude im Vergleich zu traditionellen Gebäuden: Ein Vergleich innovativer Bauweisen
In today’s rapidly developing construction industry, Metallfertigteilgebäude are gradually becoming the preferred solution for many projects, while traditional construction methods carry on millennia-old craftsmanship. What are the differences between these two construction methods? Let’s explore them from multiple perspectives.
Core Conceptual Differences
Precast metal buildings refer to a construction method that uses standardized metal components (mainly steel) prefabricated in a factory and rapidly assembled on-site. These components typically include steel columns, steel beams, metal wall panels, and roofing systems, all manufactured to precise specifications in a factory environment.
Traditional construction refers to a construction method that uses traditional materials such as brick, concrete, and wood, primarily processed and constructed on-site. This method emphasizes on-site construction techniques and relies on craftsmanship and site conditions.
Eight Key Differences Comparison
- Construction Time and Efficiency
· Precast Metal Buildings: Because components are prefabricated in a factory, only assembly is required on-site, making construction speed typically 30%-50% faster than traditional construction. A medium-sized industrial plant can have its main structure completed within weeks.
- Traditional Construction: Relies on on-site construction pace, and is affected by multiple factors including weather, material supply, and labor efficiency, resulting in longer construction periods and higher uncertainty.
- Construction Cost Structure
- Prefabricated Metal Buildings: Higher initial design costs, but through large-scale production and reduced on-site labor, overall costs are more predictable, and subsequent maintenance costs are typically lower.
- Traditional Construction: Relatively lower material costs, but high labor costs, and on-site changes can easily lead to cost overruns, making overall budget control more difficult.
- Design Flexibility and Limitations
- Prefabricated Metal Buildings: Suitable for standardized and modular designs, easily achieving large-span spaces (such as warehouses and stadiums). However, complex and personalized designs may be limited, and modification flexibility is relatively low.
- Traditional Construction: Extremely high design flexibility, capable of achieving various complex forms and details. However, large-span structures require more support, and design implementation is limited by material performance.
- Quality and Consistency
- Precast Metal Buildings: Produced in a controlled factory environment, ensuring consistent and stable quality with millimeter-level precision. Less affected by weather and site conditions.
- Traditional Buildings: Quality highly dependent on the skills of the construction team and on-site management; quality variations may exist between different projects and even different parts of the same project.
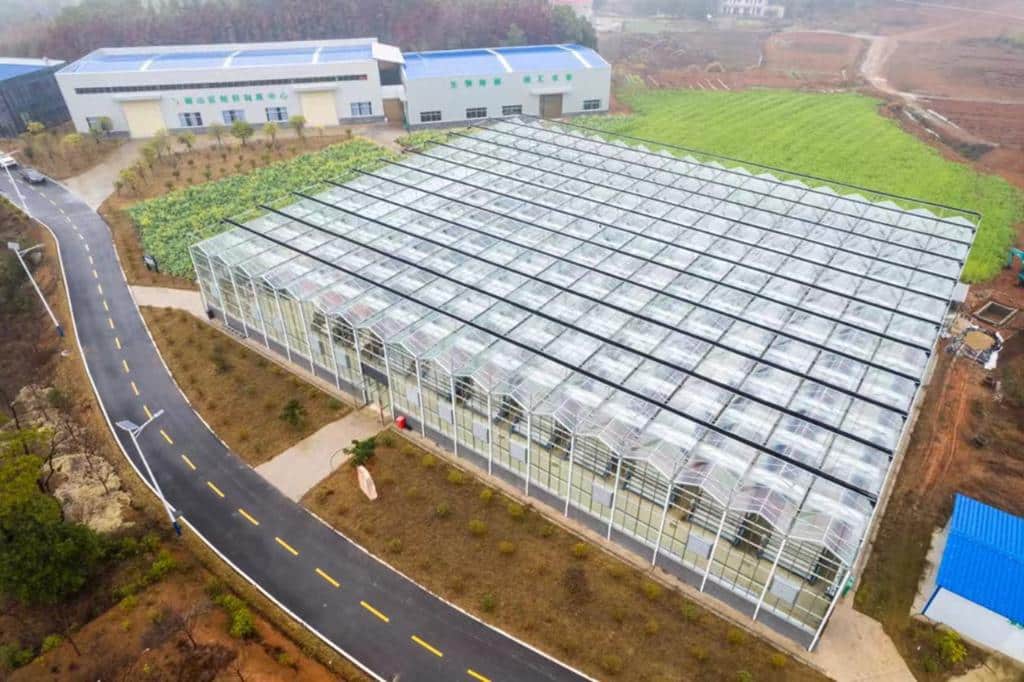

- Sustainability and Environmental Protection
- Precast Metal Buildings: Material recyclability up to 90%, reducing on-site waste by 60%-70%, and significantly reducing construction noise and pollution. However, steel production is energy-intensive.
- Traditional Buildings: Natural materials such as wood are renewable, but concrete production has high carbon emissions, and on-site construction generates a large amount of construction waste.
- Durability and Maintenance
- Precast Metal Buildings: Steel structures require coating protection for corrosion resistance, and fireproofing requires additional treatment. Excellent wind and earthquake resistance, but long-term exposure may require maintenance.
- Traditional Buildings: Masonry structures can last up to a century, but wood is susceptible to moisture and corrosion, and concrete may crack; regular maintenance needs vary depending on the material.
- Differences in Applicable Scenarios
- Prefabricated metal buildings: Particularly suitable for large-space buildings such as industrial plants, warehouses, stadiums, exhibition centers, hangars, and supermarkets.
- Traditional buildings: More suitable for residences, office buildings, schools, hospitals, historical building restoration, and projects requiring unique aesthetic expression.
- Integration of Technology and Innovation
- Prefabricated metal buildings: Highly integrated with BIM (Building Information Modeling) technology, facilitating digital design and intelligent management, representing the direction of industrialized construction.
- Traditional buildings: Gradually incorporating new technologies, but still relying on traditional craftsmanship and artisan experience, retaining more humanistic warmth.
Integrated Development Trends
It is worth noting that contemporary architectural practice is showing a trend of merging these two approaches:
- Hybrid Structural Systems: A traditional concrete substructure paired with a steel superstructure.
- Precast Concrete: Combining the advantages of prefabrication with the characteristics of traditional materials.
- Modular Buildings: Pushing the prefabrication concept to its limits to achieve overall spatial modularization.
Selection Recommendations
When choosing a construction method, consider:
- Project Requirements: Function, budget, and time constraints.
- Site Conditions: Topography, climate, and transportation limitations.
- Long-Term Planning: Service life, expansion potential, and maintenance capabilities.
- Local Resources: Material supply, availability of skilled workers, and regulatory requirements.
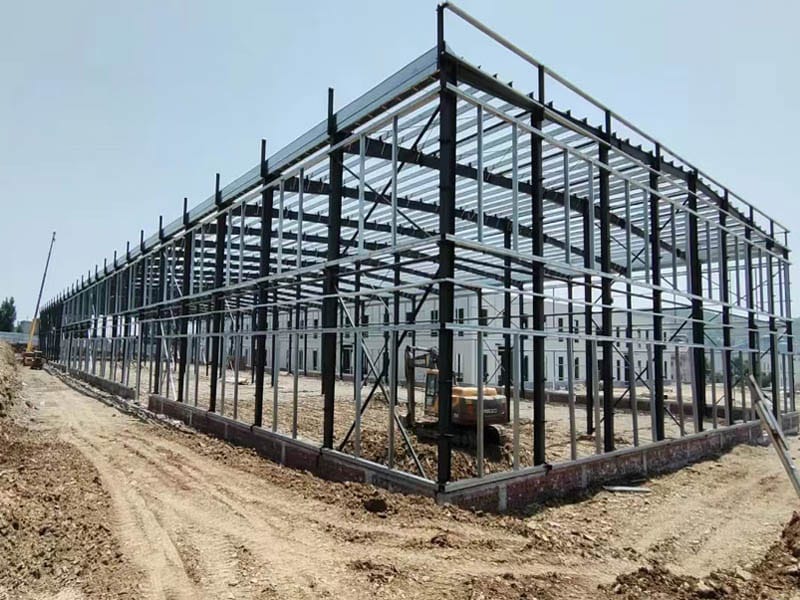

Schlussfolgerung
Precast metal architecture and traditional architecture are not simply substitutes for each other, but rather two architectural philosophies, each with its own advantages. The former represents a standardized, efficient, and industrialized future of architecture, while the latter carries the architectural tradition of personalization, artistry, and humanistic warmth. In specific projects, the wise choice is often not an either-or choice, but rather finding the optimal balance based on the project characteristics, and even creatively integrating the advantages of both.
As building technology continues to develop, both of these building methods will evolve through innovation, jointly shaping our future built environment and meeting the diverse spatial needs of human society.




WARUM SDHJIE WÄHLEN?
Der Bau maßgeschneiderter Metallkonstruktionen ist unsere Spezialität.
Weitere Projekte